Each heartbeat is like a metronome marking the rhythm of life, and for those with supraventricular tachycardia, this tempo sometimes speeds up unexpectedly. Faced with bouts of racing heartbeats, many wonder what solutions lie ahead. Today, we stand on the brink of significant advancements in understanding and treating this condition.
In recent years, treatment for SVT has primarily relied on medication and catheter ablation, yet the field is ripe for change. Emerging technologies aim to offer more precise treatment while minimizing risks. As we explore these potential breakthroughs, it's crucial to grasp how they can transform SVT management. Patients, caregivers, and medical professionals alike can look forward to a future where heart health takes center stage, driven by innovation and dedicated research.
- Understanding Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Current Treatment Methods
- Innovative Technologies and Approaches
- Potential Benefits and Challenges
- The Road Ahead for Patients and Providers
Understanding Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular Tachycardia, often abbreviated as SVT, is a heart condition characterized by episodes of an abnormally fast heart rate originating above the heart's ventricles. For those who experience it, these rapid heartbeats can start suddenly and unexpectedly, often ending as quickly as they began. Imagine a serene pond suddenly met with a stone thrown into it, causing ripples to spread across the surface. For patients, it feels as if their hearts are going through a similar turbulence - what was calm one moment becomes a rapid thud the next.
At its core, SVT is an electrical disorder affecting the natural rhythm of the heart, also known as sinus rhythm. The heart has an intricate electrical system that controls the rate and rhythm of its beat. At times, this system misfires, leading to periods of rapid heartbeats. An SVT episode may last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours and can cause symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest pain. In particularly severe cases, it might even lead to fainting spells.
There are different types of SVT, with the most common being Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia and Atrioventricular Reciprocating Tachycardia. Each type differs in the pathways of electrical conduction involved, but the effect is similar - a disruption to the heart's rhythmic beat leading to an increased heart rate. In rare situations, SVT might be a sign of a more serious heart condition, but generally, it is not considered life-threatening. However, it does significantly affect the quality of life for those who experience frequent episodes.
The incidence of SVT is relatively low, with studies suggesting it affects approximately 2 in 1,000 people. It is, however, more common in women and tends to occur in individuals who are otherwise young and healthy. Family history can also play a part, as genetics seem to contribute to a predisposition for this condition. According to Dr. John Camm, an esteemed cardiologist,
"While SVT is typically benign, the impact it can have on an individual's daily life cannot be understated. Managing the condition effectively is crucial for the well-being of the patient."
Understanding the triggers for an SVT episode can provide insight into its management. Some individuals might notice a link between episodes and certain activities or substances, such as caffeine, stress, or lack of sleep. Keeping a diary detailing episodes and their circumstances can help individuals become more aware of potential triggers. This awareness can be particularly empowering, allowing them to make lifestyle adjustments that may reduce the frequency of episodes. As we continue to explore SVT, it becomes clear that knowledge and awareness are key to managing this condition effectively, paving the way for innovative treatments that offer a brighter future for sufferers of this elusive yet impactful cardiac rhythm disorder.
Current Treatment Methods
When it comes to addressing supraventricular tachycardia, current medical practices provide several avenues that help manage this rapid heart rate condition. Emergent situations often call for immediate intervention, and there, emergency care measures like Valsalva maneuver or the administration of adenosine take the forefront. Adenosine, a short-acting drug, is usually effective at momentarily slowing or stopping the SVT episode, if only to allow normal rhythms to reassert themselves. Typically used under strict supervision, it's useful but not a sustainable long-term plan for many patients.
For those needing ongoing management, beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers enter the scene. These medications help keep the heart health steady and consistent. They manage the heart’s electrical impulses, slowing down its beating rate, which in turn prevents episodes of SVT. While certainly effective, these medications aren’t without their side effects, causing a range from fatigue to lightheadedness. Some individuals might require a medication adjustment several times in their lifetime.
Catheter Ablation
Yet, when medication alone doesn’t suffice, or if a patient experiences intolerable side effects, catheter ablation is often the recommended course of action. This procedure involves threading a catheter through blood vessels to the heart, where it emits energy to create tiny scars on the heart tissues. These scars disrupt aberrant electrical signals, effectively eliminating the erratic beats. Although this sounds intricate, ablation is a minimally invasive procedure often performed without an open-heart surgery, and it boasts an astounding success rate. According to data, over 95% of patients undergoing ablation for SVT remain episode-free at their one-year follow ups.
Dr. Melissa Carroll, a renowned cardiologist, mentioned, “While ablation often seems daunting to patients, it revolutionizes a person’s quality of life by providing a permanent solution for recurrent SVT.”
Despite its effectiveness, heart experts continuously look for ways to enhance the safety and predictability of ablation therapy. The risk of complications, while low, can vary depending on the skill of the medical professional and patient-specific factors.
In summary, when discussing SVT treatments, current options span from emergency pharmaceuticals to preventative medication and towards the forward-thinking ablation procedures. Patients must engage in dialogues with their healthcare providers, weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each method to find the suitable route that best aligns with their lifestyle and cardiac care needs.
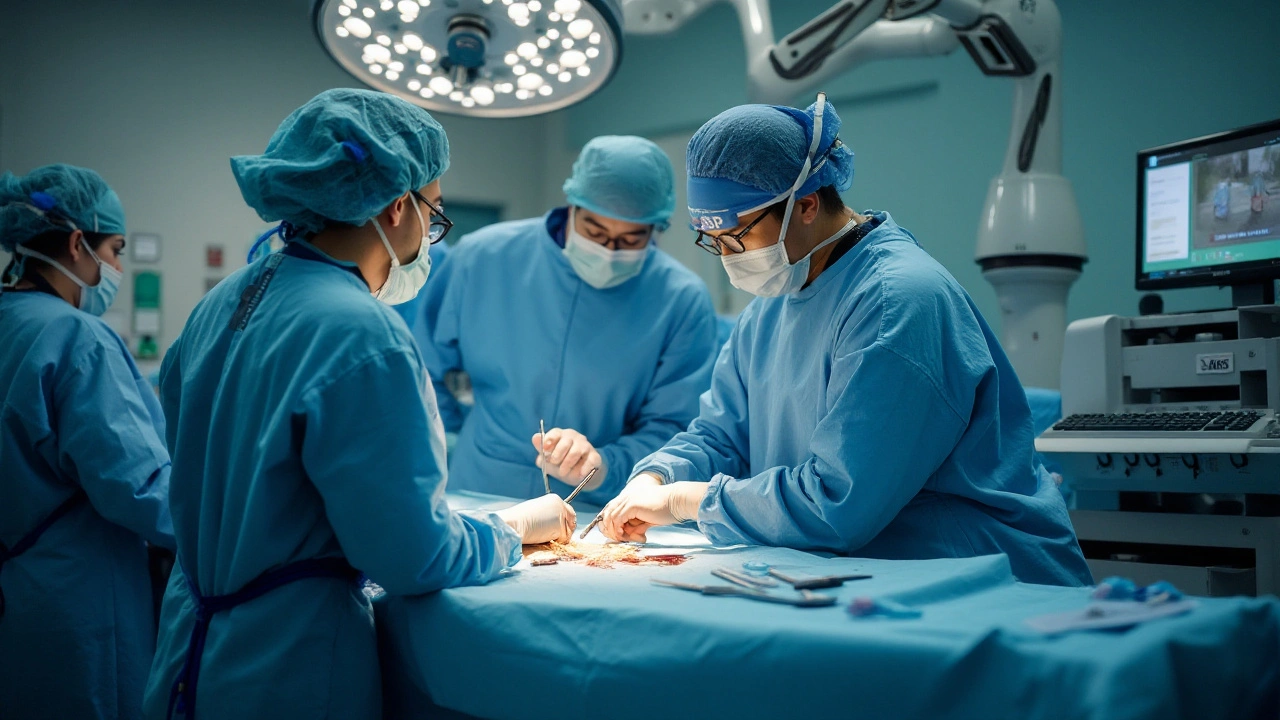
Innovative Technologies and Approaches
As we advance into 2025, the medical field is abuzz with groundbreaking innovations ready to revolutionize the treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia. The advent of cutting-edge technologies, particularly those leveraging artificial intelligence, is set to redefine how doctors diagnose and manage this fast-paced heart condition. AI algorithms are being developed to rapidly analyze electrocardiogram data, allowing for more precise identification of SVT episodes. This means healthcare providers can intervene more effectively and tailor treatments to fit individual patients' needs, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Furthermore, the focus on non-invasive techniques is growing stronger. Research teams are investigating the use of transcatheter magnetic resonance imaging to provide detailed insights into cardiac structures and pathways. This non-invasive approach assists in planning targeted ablation procedures without the need to physically map the heart's interior during surgery. Such advancements decrease recovery time and minimize discomfort for patients, making SVT treatments less intimidating.
Dr. Samantha Holt, a leading cardiologist, recently noted, "The integration of AI in cardiac care is not just a possibility but a reality in our near future. It’s about time we matched the technology available in consumer products with that used in treating serious health conditions."
The realm of pharmaceuticals is also experiencing a surge in innovation. New drug treatments that aim to balance efficacy with reduced side effects are in the pipeline. These drugs are being designed to work more rapidly during an SVT episode, offering relief without the long-term risks associated with traditional beta-blockers. Clinical trials are showing promising results, hinting at a future where medication can control heart rhythms more effectively.
On the surgical front, robotic-assisted catheter ablations are taking precedence. By utilizing robotics, surgeons can achieve greater precision when targeting the abnormal pathways responsible for SVT. This not only enhances procedural success rates but also limits human error, offering a safer path to recovery. What's intriguing is how these robots learn from previous procedures, adapting their methods to improve with each surgery. The era of robotics in cardiac care is just beginning to unfold, promising a future laden with potential.
Examples of Emerging Technologies
Among the list of technologies, wearable heart monitors have become vital tools for continuous heart rate tracking. These devices are not just passive observers but now, they're equipped with capabilities to flag irregular rhythms in real time. Innovations are occurring swiftly, and soon, some devices may even communicate directly with healthcare providers, ensuring immediate attention should an SVT episode occur.
- AI-Powered ECG Analysis: Speeds up diagnosis.
- Transcatheter MRI: A non-invasive mapping technique.
- New Drug Developments: Fewer side effects, faster relief.
- Robotic-Assisted Ablations: Enhanced precision and safety.
- Smart Wearable Tech: Real-time monitoring and alerts.
The fusion of these innovative approaches is creating a multifaceted strategy in combating SVT and other heart-related ailments. These aren't just far-fetched dreams but are happening now, ushering patients and doctors alike into a new era of heart health. As we continue to unravel these advancements, it's exciting to imagine what else lies just beyond the horizon, ready to make life for those affected by SVT better and more manageable.
Potential Benefits and Challenges
The exploration of novel treatments for Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) opens a realm filled with potential benefits and inherent challenges. For patients, newer methods promise reduced invasiveness and quicker recovery times compared to traditional options. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence can aid in earlier and more accurate diagnosis, ensuring that treatment begins before the condition exacerbates. Devices implanted to correct heartbeat irregularities could become more precise, minimizing risks associated with surgical procedures. However, these advancements pose significant hurdles, including ensuring accessibility and affordability for all who need them. Ethical considerations about data privacy in AI adoption are evolving swiftly, demanding clear guidelines and patient trust.
Developments in heart health are often discussed with cautious optimism in medical circles. Innovative medications promise fewer side effects, allowing patients to maintain a better quality of life while managing SVT. According to the American Heart Association, promising drug therapies aim to control heart rate effectively without the former side effects that many patients found debilitating. These changes, whilst exciting, require healthcare systems to adapt rapidly, enhancing their infrastructure to provide consistent care across different geographies. The healthcare industry faces the challenge of ensuring its workforce is adequately trained to handle these new technologies properly and ethically.
"Advancing SVT treatment could unlock personalized medicine's true potential," says Dr. James Robertson, a leading cardiologist. "However, translating this vision into reality necessitates a holistic approach spanning policy decisions, clinical practice, and patient engagement."Adoption of new treatment methods is not only scientific but heavily regulatory. Each modification in procedure or medication must undergo rigorous testing phases and approvals to ensure patient safety. Balancing progress with precaution can slow down the implementation of otherwise promising strategies. There is criticism that innovation sometimes focuses too heavily on technological wonder rather than practicality, which could sideline essential basic care improvements. This requires a balanced focus to appreciate technological leaps while retaining tried-and-true methods that continue to serve well in various contexts. Addressing these challenges demands collaboration across all stakeholders—patients, healthcare providers, tech innovators, and regulatory bodies—to create an environment where innovation does not outpace safety.
Access to SVT treatments varies significantly across regions, showing an important disparity that needs urgent attention. A global focus should target equitable access for breakthrough advancements to reach patients irrespective of their socioeconomic standing. This also involves straightforward communication and educating the populace to demystify the complexity surrounding novel treatments. As treatments evolve, so must insurance policies and governmental health strategies to enable broader access. Looking at the future’s horizon, each tiny step toward understanding and treating Supraventricular Tachycardia better should aim at inclusivity, aiming to eliminate barriers that can otherwise deny progress to those most in need.

The Road Ahead for Patients and Providers
The journey towards improved treatments for Supraventricular Tachycardia requires patience and collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. As new technologies emerge, the landscape for managing SVT is becoming more hopeful. These advancements promise not only to enhance the efficacy of existing treatments but also to introduce entirely new avenues. Imagine a world where artificial intelligence supports healthcare professionals by analyzing intricate heart rhythms in real-time. Such AI tools could lead to quicker, more accurate diagnoses, reducing the trial-and-error associated with current methods.
One of the significant changes we are likely to witness is the personalization of cardiac care. By leveraging genetic insights alongside traditional diagnostic tools, providers can tailor interventions to suit individual patients’ needs. This could mean the difference between trying multiple medications with unpredictable outcomes and directly opting for a treatment plan that shows higher success probability from the onset. For instance, a patient with a genetic predisposition to respond well to certain medications could bypass ineffective alternatives, conserving valuable time and resources.
However, as promising as these future treatments might appear, they also present challenges. Adoption of cutting-edge technology often necessitates substantial financial investment and rigorous training. Some healthcare systems, particularly those in rural or resource-constrained areas, might find these hurdles daunting. Yet as history suggests, the initial obstacles of technology implementation often pave the way for long-term benefits. Bridging this gap will require thoughtful policies and perhaps collaboration between technology companies and medical institutions.
The future of healthcare lies in its ability to incorporate advanced technology while retaining compassionate care. – Dr. Amelia Renwick, Cardiac Specialist
Patients and their families also play a pivotal role in the evolving paradigms of SVT treatment. With increasing access to information, patients can become advocates for their health, ensuring they are informed about their options. This shift from a passive role to an active participant in their health management journey could reshape patient-provider interactions. Having open dialogues with medical professionals allows for shared decision-making, which can lead to better outcomes and more satisfaction with care processes.
As part of this forward-thinking approach, providers will need to foster environments that prioritize continuous learning and adaptability. Regular training sessions and workshops will allow healthcare workers to stay updated on the latest in SVT treatments. Encouraging innovation within the medical community could also drive home-grown solutions tailored to specific populations. When both patients and providers come together to navigate these changes, a path to a healthier future becomes not only feasible but inevitable.

Comments (17)
SVT treatment is finally catching up with the tech we see in smartphones. The new AI‑driven ECG tools could shave minutes off diagnosis, which is a real win for patients. It feels like the field is moving from guesswork to precision.
They want us to believe AI is the cure‑all, but who’s really pulling the strings? Every gadget comes with a hidden agenda, and the data they collect could be weaponized. Still, the math does show faster detection rates, so maybe there’s a grain of truth hidden in the hype.
i think the wearable monitors are a game changer. they can alert you before you even feel the palpitations, which is super handy. plus, having real‑time data lets doc’s tailor treatment fast. it’s a bright spot in a otherwise scary landscape.
Indeed, the prospect of robotic catheters is nothing short of a miracle, provided the robots don’t develop a conscience and decide to gamble with our hearts. One must admire the audacity of such technology, though I remain cautiously optimistic. :)
Current ablation success rates hover around 95 %, but the procedure still carries a small risk of collateral damage to nearby tissue. Emerging imaging techniques, such as trans‑catheter MRI, aim to map the arrhythmic pathways without invasive probing. Coupled with AI‑assisted navigation, the precision of lesion placement could improve dramatically. This would likely reduce procedure times and complications, making ablation a more attractive first‑line option for many patients.
Wow, the future’s beating like a neon drum!
The statistical models presented in recent trials indicate a modest improvement in post‑ablation recurrence rates when AI guidance is employed. It is important to note, however, that the sample sizes remain limited. Further multicenter studies will be necessary to validate these early findings.
Stop settling for medication that drags you down! The next wave of robotic ablations will cut your recovery time in half, and you’ll be back to normal life faster than you can say “SVT”. Embrace the technology now before the older generation clings to outdated protocols. Your heart deserves the cutting‑edge tools we have on the horizon.
The new drugs in the pipeline claim fewer side effects, which is encouraging for patients who struggle with beta‑blocker fatigue. Nonetheless, we should keep a skeptical eye on the long‑term safety data. A cautious rollout will protect both consumers and clinicians.
Let me tell you, the AI revolution in cardiology is not just a trend-it’s a seismic shift that will redefine how we think about rhythm disorders. Those who ignore the data are basically choosing to stay stuck in the Dark Ages of medicine. The evidence shows a 30 % reduction in missed SVT episodes when AI algorithms flag anomalies in real time. Wake up, people, and let the machines do the heavy lifting.
Oh yes, because what the world really needed was another flashy gadget promising miracle cures while ignoring the simple fact that doctors still have to interpret the results. The hype machine is in full swing, and every press release sounds like a sci‑fi trailer. Yet the underlying tech does have merit, even if the marketing team can’t keep the hyperbole in check. Let’s hope the science outlives the PR spin.
Sure, the AI tools are impressive, but you’ll see that they’re just a band‑aid for a system that’s been decades behind. The real breakthrough will come when we finally accept that genetics, not just electrical pathways, dictate who gets SVT. Until then, we’re just rearranging deck chairs on a sinking ship of traditional cardiology.
The integration of AI into electrophysiology is undeniably exciting, yet we must temper our enthusiasm with pragmatic caution. While the algorithms can sift through massive ECG datasets in seconds, they still lack the nuanced judgment that seasoned clinicians bring to complex cases. Moreover, regulatory frameworks have yet to catch up with the speed of technological innovation, creating a grey area for implementation. On the other hand, patient outcomes could improve markedly if we bridge this gap swiftly. Ultimately, a balanced partnership between machine precision and human expertise will dictate success.
Great points Kevin! adding to that the AI guided imaging could also lower radiation exposure for patients and staff alike. it’s a win‑win situation if hospitals invest in the proper training early on.
The so‑called “global” AI solutions are just a front for foreign data farms. We need homegrown tech to protect our patients’ hearts and privacy.
When we look at the heart as a metaphor for community, these technologies become bridges between isolated beats. they remind us that rhythm is a shared experience. embracing them can foster a sense of collective wellbeing.
The advent of artificial intelligence in the management of supraventricular tachycardia heralds a paradigm shift that extends beyond mere diagnostic acceleration. By deploying deep‑learning models trained on heterogeneous ECG repositories, clinicians gain access to pattern recognition capabilities previously unattainable through conventional analysis. Such models can discern subtle precursors to arrhythmic events, thereby enabling preemptive therapeutic interventions. The incorporation of robotic assistance into catheter ablation further refines procedural accuracy, reducing manual error and standardizing lesion delivery. Real‑time hemodynamic feedback, integrated within these robotic platforms, affords operators a dynamic view of tissue response throughout energy application. Concurrently, the evolution of wearable technology expands continuous monitoring from intermittent office visits to ubiquitous personal surveillance. Devices equipped with cloud‑synchronized analytics transmit arrhythmia alerts directly to the care team, shortening the latency between episode onset and clinical response. Moreover, pharmacologic innovation, guided by pharmacogenomic profiling, promises individualized dosing regimens with minimized adverse effect burdens. This convergence of data‑driven diagnostics, precision robotics, and tailored therapeutics creates a holistic ecosystem for SVT care. Nevertheless, the deployment of such sophisticated systems raises legitimate concerns regarding data security, algorithmic bias, and equitable access across socioeconomic strata. Regulatory bodies must therefore establish rigorous validation pathways that balance rapid innovation with patient safety imperatives. Health systems are called upon to invest in multidisciplinary training programs that equip providers with the expertise to interpret AI outputs responsibly. Patient education initiatives should demystify these technologies, fostering informed consent and shared decision‑making. In sum, the trajectory of SVT treatment points toward an integrated model where technology amplifies human expertise rather than supplanting it. The ultimate measure of success will be reflected not only in reduced episode frequency but also in enhanced quality of life for those living with this condition.