Hair Loss Treatment Recommendation Tool
Find Your Best Hair Loss Treatment
Answer a few questions to get personalized recommendations based on your medical history, budget, and treatment preferences.
When it comes to tackling male‑pattern baldness, the market is crowded with pills, liquids, and topical solutions. Dutanol (dutasteride) has gained a reputation as a powerhouse 5‑alpha‑reductase inhibitor, but is it truly the best fit for every user? This guide breaks down how Dutanol works, weighs its pros and cons, and stacks it against the most common alternatives - Finasteride, Minoxidil, Saw Palmetto, and Ketoconazole - so you can decide which regimen aligns with your goals, budget, and tolerance.
What is Dutanol (Dutasteride)?
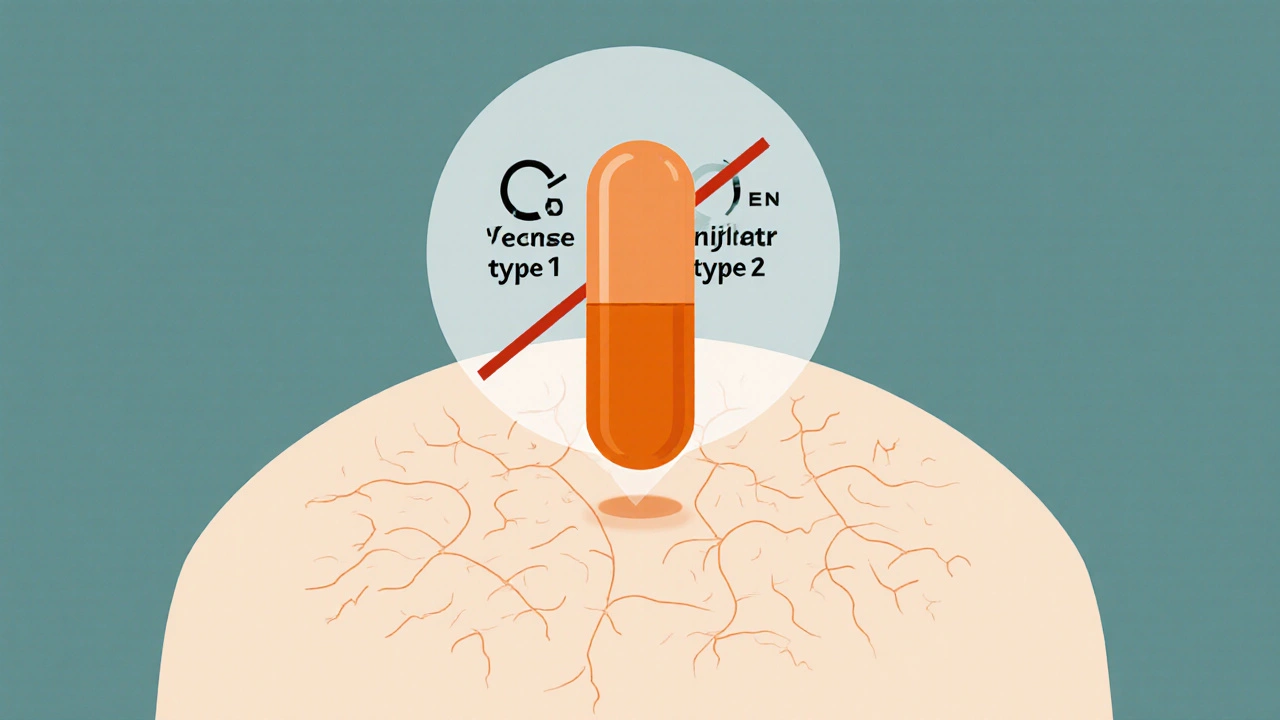
Dutanol is the brand name for dutasteride, a synthetic steroid that selectively blocks both type‑1 and type‑2 isoforms of the enzyme 5‑alpha‑reductase. By shutting down the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), it dramatically lowers scalp DHT levels, the main driver of follicular miniaturization in androgenetic alopecia.
How Dutanol Works at the Molecular Level
The enzyme 5‑alpha‑reductase exists in two isoforms: type 1, primarily found in the scalp and skin, and type 2, predominant in the prostate. Dutanol binds irreversibly to the active sites of both isoforms, delivering up to a 90 % reduction in serum DHT after 6 weeks of daily 0.5 mg dosing. This dual‑action contrast with Finasteride, which only targets type 2, explains why many clinicians observe faster hair‑density gains with Dutanol.
Key Benefits and Risks of Dutanol
- Significant DHT suppression (≈ 90 % vs. ≈ 70 % for Finasteride).
- Clinical studies show a 30‑40 % increase in hair count after 12 months of continuous use.
- Once‑daily oral capsule - no messy topical application.
- Potential sexual side effects: decreased libido, erectile dysfunction (seen in 2‑5 % of users).
- Rare but reported: gynecomastia and mood changes.
- Long‑term safety data are robust for prostate‑cancer indications, yet long‑term dermatologic outcomes remain under‑studied.
Top Alternative Treatments
Before you lock in a prescription, it helps to know what else is out there. Below are the four most frequently discussed alternatives:
- Finasteride - a 5‑alpha‑reductase type 2 inhibitor, approved at 1 mg daily for hair loss. It offers solid efficacy with a slightly lower DHT suppression rate.
- Minoxidil - a topical vasodilator available in 2 % and 5 % solutions. It works by prolonging the anagen phase of hair growth rather than altering hormones.
- Saw Palmetto - a plant‑derived extract thought to inhibit type 1 5‑alpha‑reductase. It’s popular among those who prefer “natural” options, though clinical evidence is mixed.
- Ketoconazole - an antifungal shampoo (2 % or 1 %) that also reduces scalp DHT and tackles inflammation. It’s best used as an adjunct rather than a stand‑alone therapy.
Side‑by‑Side Comparison
| Medication | Primary Mechanism | Typical Dose | Approved Indication | Common Side Effects | Average Annual Cost (US$) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dutanol | Dual 5‑alpha‑reductase inhibition (type 1 & 2) | 0.5 mg oral daily | Androgenetic alopecia (men) | Sexual dysfunction, breast tenderness, mood changes | ≈ $800 |
| Finasteride | Selective type 2 inhibition | 1 mg oral daily | Androgenetic alopecia (men) | Decreased libido, ejaculatory issues | ≈ $500 |
| Minoxidil | Vasodilation & anagen phase extension | 2 % or 5 % topical solution twice daily | Androgenetic alopecia (men & women) | Scalp irritation, unwanted facial hair | ≈ $200 |
| Saw Palmetto | Natural type 1 inhibition (weak) | 320 mg oral capsule daily | Dietary supplement for hair health | Gastrointestinal upset | ≈ $150 |
| Ketoconazole | Antifungal + DHT reduction | 2 % shampoo 2-3×/week | Scalp psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis | Dryness, itching | ≈ $120 |
The table highlights three practical axes: potency (how much DHT it removes), route of administration, and price point. If you need the strongest DHT knock‑down and can handle a prescription pill, Dutanol leads the pack. If you prefer over‑the‑counter and minimal systemic exposure, Minoxidil or Ketoconazole are sensible picks.

Choosing the Right Option for Your Lifestyle
Decision‑making becomes easier when you map personal constraints to medication traits.
- Medical History: Men with prostate issues often already take dutasteride for BPH; adding it for hair loss may simplify therapy. Those with a history of sexual dysfunction should discuss risk mitigation with a doctor.
- Budget: If out‑of‑pocket cost exceeds your comfort zone, a Minoxidil‑first approach can still deliver visible regrowth for many users.
- Compliance Preference: Daily pills demand strict adherence. Topicals require twice‑daily routine; some find it easier to remember a morning shower step.
- Desired Speed: Clinical trials show Dutanol can add 10‑15 % more hair density at 12 months versus Finasteride. Expect noticeable changes after 6 months for most oral agents; Minoxidil may need 4‑6 months.
- Combination Strategies: Many dermatologists prescribe a low‑dose oral inhibitor (dutasteride or finasteride) plus twice‑daily 5 % Minoxidil. The synergy boosts both follicle survival and growth rate.
Ultimately, the “best” choice is the one you can stick with consistently while staying within your safety parameters.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can women use Dutanol for hair loss?
Dutanol is not approved for female pattern hair loss because systemic DHT suppression can cause hormonal imbalance. Women typically rely on Minoxidil 2 % or low‑dose oral anti‑androgens under specialist supervision.
How long does it take to see results with Dutanol?
Most patients notice a reduction in shedding after 8‑12 weeks and measurable hair‑count gains after 6‑12 months. Patience is key; stopping the drug will likely reverse any gains within months.
Is it safe to combine Dutanol with Minoxidil?
Yes, the combination is frequently prescribed because the mechanisms complement each other. Monitor for scalp irritation from Minoxidil and discuss any sexual side effects from Dutanol with your clinician.
What are the cost differences between Dutanol and Finasteride?
As of 2025, Dutanol averages $800 per year in the U.S., while Finasteride sits around $500. Insurance may cover Finasteride more readily because of longer market presence, but some plans also reimburse dutasteride for BPH indications.
Are there natural alternatives that work as well as Dutanol?
Saw Palmetto and pumpkin seed oil are the most studied botanicals. Evidence suggests modest DHT reduction (≈ 20‑30 %) but far less than dutasteride’s 90 % drop. They may be useful adjuncts for men worried about prescription side effects.
Choosing a hair‑loss regimen involves balancing potency, safety, cost, and personal convenience. Dutanol remains the most potent oral option for men who can tolerate its side‑effect profile, while alternatives like Finasteride, Minoxidil, Saw Palmetto, and Ketoconazole each offer niche advantages. Consult a dermatologist or primary‑care provider to map your health history onto the matrix above, and you’ll be set on a path toward fuller hair.

Comments (11)
If you’re not willing to sacrifice a little comfort for a thicker crown, you’re simply choosing complacency over progress.
I get why the side‑effects worry you; many find the trade‑off worth it when they see steady regrowth, especially if they stick to the regimen for at least a year.
In clinical terms, dutasteride’s dual‑isoform blockade yields roughly a 90 % DHT knock‑down, which is a no‑brainer for anyone seeking maximal efficacy, even if the pharma‑giants don’t shout about it.
Permit me to underscore that a disciplined combination of oral inhibitor and topical minoxidil has consistently produced the most robust outcomes; adhering to a structured protocol is paramount for success.
While you extol the virtues of “structured protocol,” one must recognize that the underlying research is often curated by a clandestine consortium of dermatological elites who suppress alternative narratives.
It’s maddening how the same board that pushes pricey shampoos also silences honest discussion about long‑term hormonal impacts.
Empirically, a 0.5 mg daily dose of dutasteride reduces serum DHT by approximately 90 % within six weeks, whereas finasteride at 1 mg achieves about 70 %; this differential translates to a statistically significant increase in hair count after twelve months, as documented in multiple Phase III trials.
The moral imperative for anyone contemplating hair‑loss treatment is to seek truth above convenience.
Few pharmaceuticals are presented without an agenda, and dutasteride is no exception.
Its potency in suppressing DHT is undeniable, yet the discourse often omits the lived experiences of those burdened by side effects.
Sexual dysfunction, albeit reported in a minority, can erode personal relationships and mental health.
When a medication meddles with hormonal pathways, the ethical responsibility lies with both prescriber and patient to weigh benefits against potential harms.
Furthermore, the long‑term dermatologic safety profile remains less robust than the prostate‑cancer data that underpins its approval.
Patients must demand transparent longitudinal studies that extend beyond the typical twelve‑month horizon.
Cost considerations also factor into ethical decision‑making, as an $800 annual price tag excludes many from access.
Insurance coverage disparities amplify inequities, favoring those with privileged employment benefits.
Consequently, the narrative that dutasteride is a universal solution is a disservice to the diverse population it claims to serve.
Alternative therapies-whether minoxidil, ketoconazole, or phytochemicals-offer varying degrees of efficacy without the same systemic risks.
Integrative approaches can mitigate side‑effects while still delivering measurable regrowth.
Ultimately, informed consent is not a mere formality but a cornerstone of ethical medical practice.
Patients should be equipped with comprehensive data, including comparative studies, side‑effect prevalence, and cost analyses.
Only then can they make a decision that aligns with their values and health priorities.
Neglecting this responsibility perpetuates a cycle of exploitation under the guise of aesthetic improvement.
The regimen works only if you stay consistent.
The data suggests moderate DHT reduction improves outcomes
While the average consumer chases cheap fixes, true connoisseurs recognize that only rigorously vetted pharmaceuticals merit consideration; domestically produced formulations further guarantee adherence to stringent standards.